Up until the start of the last decade, the main drivers of research comprised directly collected primary data. However, as more and more digital data has been generated alongside better practices and more and more contributions to public data repositories, secondary data (that is contributed and stored in large online databases) has now become one of the main tools for researchers around the world. Secondary sources are now used to find relevant data as well as to advance knowledge much faster than before.
Databases have therefore become essential components of research projects. The development of digital infrastructure has also led to easier ways to store and utilize data in digital formats.
Online databases can be used to find relevant data faster without the expense of reproducing experiments and physical research. This makes data more available to researchers and society in general.
In order to understand how to efficiently use databases for research, it is first necessary to determine what such databases actually are. In this context, a database is a combination of structured, stored data and the infrastructure to support storage. This infrastructure generally comprises applications and software enabling storage as well as associated computers.
Research institutions and companies today enable researchers to work with different infrastructures that enable the aggregation of more databases for many different purposes. These aggregates are called data repositories; this is one of the most important terms we use when trying to understand how to use databases efficiently.
There are two main uses for such research repositories.
- Finding data relevant for a research project
- Contributing data for transparency and reuse
These two main database repository uses are key for enabling processes as well as for helping research to be carried out in the first place. Thus, to simplify how databases can help you with data related problems, the following graphs address these specific questions.
How can database repositories help researchers answer some of their most important data questions.
Finding data relevant to research
Finding relevant data in online databases is now very straightforward for researchers. Indeed, video tutorials are often available regarding how to use a data platform; ensure you view those that are available. One further aspect which is very important before starting a data search is to define relevant research areas which might be associated with data; this means you’ll need to know the domains related to data as well as the relevant terms that should put on paper or as a digital document for further use. It's recommended to organize these relevant terms and domain information in a simple Word, Notepad, or Excel file. These can later be included in the parts of the data search journey.
- Predefining keywords
- Using database search features
- Filtering results
Here is an example of a data repository interface using the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) platform.
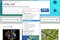
The first step for every researcher should therefore be to define data relevant for a given research project. This means that predefined data should be used to address a given research question. There are multiple aspects to this first step; one is to make a list of keywords which will be used to discover the data. These keywords are typically contained in the heading of the research project, as well as in the abstract, results, and discussion of the manuscript.
Here is an example of the keywords that would be used to find relevant Insulin/Type II Diabetes data - [INSULIN, HORMONE, DIABETES,TYPE 2, PROTEIN]. Some of these keywords can also be used for filtering, so results can be filtered using a dropdown option. Subsequent results then output only gene expression data and so other words need to be entered into the search box to find relevant data.
Here are some links to other data repositories focused on different areas of the Natural Sciences, as well as Social Sciences and Engineering. Most of these repositories support open science and facilitate finding data for researchers within their specific domains.
- NCBI - Biomedical and Genomic Data
- EMBL - Biomedical and Molecular Biology data
- Uniprot - Protein/Amino acids data
- Reactome - Biological interaction and annotation data
- Paleoportal - Paleontology data
- Chembl - Cheminformatics data
- Re3data - From Social and Humanity Science to Medical datasets
- Dhsprogram - Spatial/Geography data repository
- Harvard Dataverse - A collection of datasets and dataverses from different areas ( Life Sciences, Law, Engineering, Social Science and many other
- Openicspr - Social, Behavioral and Health related databases
- Zenodo - Life Science data
- CERN data portal - Physics data
- HEP Data - Physics data
- Google datasets is an efficient way to search for different data sources online and leverage this powerful search engine to find applicable data.
Retrieving data
- Evaluate available files - Once you have identified that the data you need is present in a repository, the next step is to evaluate its amount and characteristics. In order to do this, it is necessary to ensure that data is present in a complete form, there is enough to answer your research questions, and that the primary source authors have provided all the relevant information about the data which make it applicable for your use. Finally, always look for terms of use for data, contained in the relevant License of use.
- Select the right data format
- Download data for future use
Contributing data for transparency and reuse
The second way to effectively use the databases and their repositories is to upload and contribute the data if needed and applicable. Contributing the data means making it available for other researchers to reuse.
This is one of the best ways to improve certain research areas., It enables many researchers to perform analyses from different angles, tools, and methods. All the results publications should cite the original data contributor, so this principle enables both the better use of Research data and improves the academic visibility and results of the contributor.
Providing the relevant information about the data
One of the most important aspects of publishing the data on any database is the Meta-data. This data will show the maximal extent of the context around the data being published to all future users. Any reuse of the public data is highly dependent on what this data represents, what experiments and methods were used, what terms are used in the dataset and many other details.
Defining the license for the data
Before you publish any data, decide which conditions you want to make the data available to others. Define the license under which others can use the data in the future. Before setting the license, you must know which licenses are commonly used and what their terms are.
Here are some licenses to keep in mind:
- CC family
- Apache 2.0
- MIT
- BSD - 2
- BSD -3
- GNU
- EU Public 1.1
- ISC
- Educational community license
CC family, Apache, MIT, GNU are types of permissive licenses. They are considered as families of licenses and allow for public reuse of the data. Licenses enable and facilitate dissemination of the data for future research and reuse.
Even if the data is shared publicly reuse, citing the data is always the best practice. Similarly to the authors of the research, data authors are also contributors and are cited whenever their data is used.
Creating your own database repository for Research
One of the best platforms to create your own data repository is GitHub. Even though GitHub is famous as a code sharing and software development platform, one of its best features is storing and sharing data.
Researchers can create their own repositories where they can store and share the data. Before actually storing data, define whether the data is private or non-sharable to others, or public data which can be shared with others.
A data repository on GitHub is also one of the best ways to organize it and keep all the relevant information about the data revisions, changes and integrate the data for future reuse. Other sites where similar options are available for researchers are Gitlab, SourceForge, Launchpad.

Finally, storing the datasets, data information, research method information, codes and supplementary files in a data repository platform like GitHub improves the workflow for any research project. They make sure that data is stored in a safe place and well organized. Before the research is published, it is always good to keep the repositories private (on Github there are 2 options: private or public repositories). Once the study is published, authors can decide if their repositories can be made with the public setting and contribute to transparency and potential data reuse.
Note: Digitalization of the data has made the online databases one of the main tools for data storage, analysis and organization. There are more and more digital data created every day. Skills in using the databases to find the data, store and organize it are essential for any present or future researcher.
